In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, staying connected is more crucial than ever. The terms 5G and 4G are frequently used, often interchangeably, but understanding the difference between 5G and 4G is essential for making informed decisions about your mobile connectivity. This article will delve into the core distinctions between these two generations of cellular network technology, highlighting the advantages of 5G over 4G, and exploring the implications for businesses and consumers alike. From 5G speed and 4G speed comparisons to the impact on applications like 5G internet and 4G internet, we’ll cover the key aspects to help you navigate the world of mobile broadband.
Are you curious about the difference between 5G and 4G? Beyond just faster speeds, the transition from 4G to 5G represents a significant leap forward in cellular network capabilities. This article will dissect the core technologies behind 5G and 4G, explaining how 5G‘s advancements translate into tangible benefits. We’ll explore the real-world implications of 5G speed vs. 4G speed, the impact on 5G internet and 4G internet experiences, and the transformative potential of 5G across various industries. By understanding the difference between 5G and 4G, you’ll be better equipped to harness the power of these technologies.
Basics of Mobile Network Generations
Mobile network generations, often shortened to just “G,” represent significant advancements in cellular technology. Each new generation brings faster speeds, lower latency, and improved capabilities.
The evolution from 1G to the current 5G has dramatically changed how we communicate and access information. 1G offered only analog voice calls. 2G introduced digital voice and texting. 3G ushered in mobile internet access. 4G LTE significantly increased data speeds, enabling video streaming and other data-intensive applications. Now, 5G promises even faster speeds, ultra-low latency, and the ability to connect billions of devices.
These advancements are driven by continuous innovations in areas like radio frequencies, network architecture, and data encoding. Understanding the basics of each generation helps clarify the progress and potential of mobile technology.
Speed Comparison

One of the most significant differences between 5G and 4G lies in their speed capabilities. 5G offers significantly faster download and upload speeds compared to its predecessor.
4G typically delivers peak download speeds of up to 100 Mbps, while 5G can theoretically reach speeds of up to 20 Gbps, although real-world speeds are currently much lower, often in the hundreds of Mbps. This dramatic increase in speed enables users to download large files, stream high-definition videos, and access data-intensive applications much more quickly.
This difference in speed is due to several factors, including the use of higher frequency bands by 5G, as well as more efficient use of the spectrum. Latency, the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction for its transfer, is also significantly reduced in 5G, further enhancing the user experience for activities like online gaming and video conferencing.
Latency and Reliability
A key differentiator between 5G and 4G lies in their latency and reliability. Latency refers to the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction for its transfer. 5G offers significantly lower latency than 4G, meaning faster response times.
Reliability, in this context, refers to the consistency of the network connection. 5G networks are designed for greater reliability than their 4G predecessors. This means fewer dropped connections and a more stable experience for users, particularly in areas with high network congestion.
This enhanced reliability makes 5G suitable for applications requiring real-time responsiveness, such as remote surgery and autonomous vehicles. Lower latency allows for near instantaneous communication, crucial for these types of applications.
Battery Usage Considerations
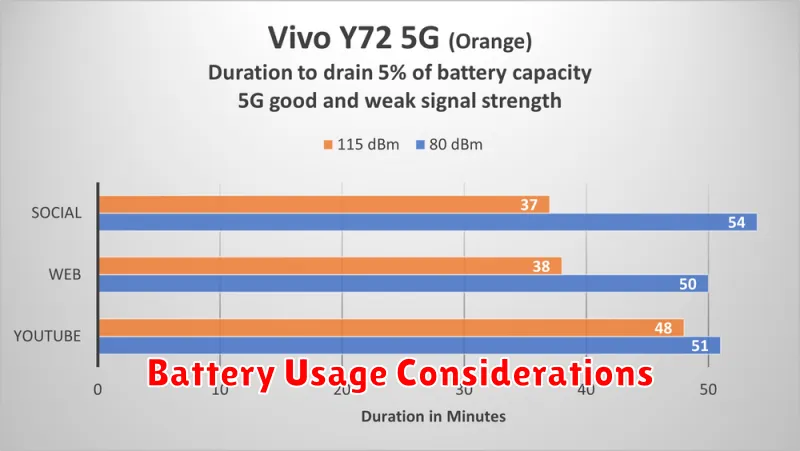
A key difference between 5G and 4G lies in their impact on device battery life. Generally, 5G consumes more power than 4G. This is due to several factors, including the higher frequency bands used by 5G, which require more energy to transmit data. Additionally, 5G’s advanced features, such as beamforming and MIMO (multiple-input and multiple-output) technology, also contribute to increased power consumption.
The extent of battery drain varies based on several factors. Network conditions play a significant role; a weaker 5G signal will force the device to work harder to maintain a connection, thus depleting battery life faster. Device usage is another important consideration. Streaming high-definition video or playing graphically demanding games will drain the battery more quickly on both 4G and 5G, with a more pronounced impact on 5G. Furthermore, the specific device and its power management capabilities also influence battery performance.
Device Compatibility
A key difference between 5G and 4G lies in device compatibility. 5G requires a 5G-compatible device, while 4G operates on a wider range of devices. Older devices designed solely for 3G or 4G networks cannot access 5G networks.
Conversely, 5G-enabled devices are backward compatible with 4G and 3G networks. This allows 5G devices to connect to available 4G or 3G services in areas where 5G coverage is not yet established. This backward compatibility ensures a seamless transition for users adopting 5G technology.

